Repeating Group
Repeating Group is an element used to detect repeating groups of elements (the number of repetitions may not be known in advance). A group may repeat either on one and the same page or on a multi-page sheet.
In the project tree, Repeating Group elements are marked with  .
.
If a group of elements recurs within a document, you may describe its properties only once, and specify the number of possible repetitions rather than describe each group separately.
Possible uses:
- Searching for a running name on each page of a multi-page document
- Searching for repeating data, where the exact number of repeating instances is not known in advance (e.g. tables with complex rows)
A Repeating Group element is different from a Group element in that it has certain additional search constraints and a repetition parameter.
After a FlexiLayout is applied and a repeating group of elements is detected, the captions of some of the elements may overlap with the image. To hide the captions, right-click anywhere in the Image window and clear the Show Captions of Regions on Image option on the shortcut menu.
The properties of a Repeating Group element which define the parameters of the object to be detected
The properties that define the parameters of the object to be detected are specified on the Repeating Group tab of the element's Properties dialog box. To open the Properties dialog box, right-click the element in the FlexiLayout window and select Properties... on the shortcut menu.
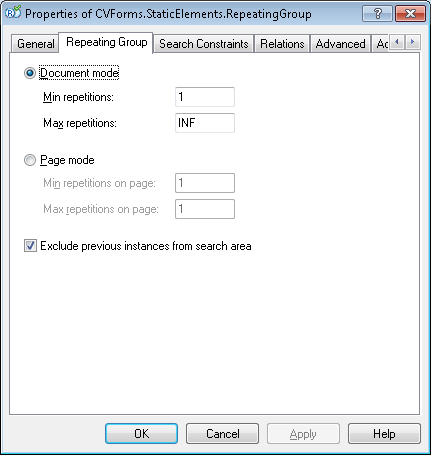
Show Properties dialog tab, Repeating Group tab
There are two ways to search for instances of a repeating group - either in the entire document or on individual pages. Correspondingly, you specify the minimum and maximum number of group instances either for the entire document or for individual pages.
If a repeating group contains a required element, it serves as the identifier for matching the instance. For example, if you specify the name of a repeating group of fields as a required element, the program will create as many instances as the number of names it detects.
The quality of the null hypothesis is specified for one instance and not for the entire set of instances. This parameter also serves as a criterion for forming an instance: if the quality of the generated hypothesis is lower than the quality of the null hypothesis, no instance is formed.
To search for group instances in the entire document, select the Document mode option and specify the following:
- Min repetitions - the minimum number of group instances in the document
- Max repetitions - the maximum number of group instances in the document
If the possible number of group instances is not detected in the document, the Repeating Group is considered not detected. If the maximum number of instances is detected, the search stops. In this default search mode, a group instance (which, just like the usual Group element, consists of hypotheses for its subelements) may stretch over several pages of the document.
To search for group instances on individual pages, select the Page mode option. In this mode, each instance may occur only with one page of the document. You can use this mode to search for a running name, for example. In this mode, the search is carried out top to bottom, from the first possible page to the last one. The following search parameters are available in this mode:
- Min repetitions on page – specifies the minimum number of instances per page. If the minimum number of instances is not detected on the current page, the Repeating Group is considered not detected.
- Max repetitions on page – specifies the maximum number of instances per page. If a required number of instances is detected on the current page, the search stops on the current page and continues on the next one.
Location of instances
The following constraint is imposed on the instances of an element: no two instances may intersect. This is achieved by forcibly excluding (Exclude) the already detected instances. On the Relations tab, you can set constraints for the next instance based on already detected instances.
For example, you can tell the program that it must look for each next instance below the previous one. On the Relations tab, set the BELOW constraint for your Repeating Group:
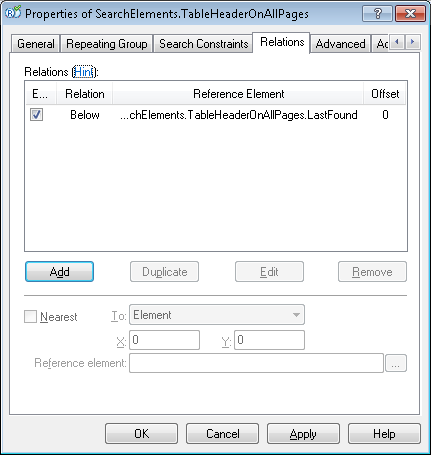
 Note.It recommended that you specify a Nearest relation for a subelement in the group, defining its position relative to the to edge of the page. Otherwise, the program will select the next instance of the group by applying the best quality criterion to all the instances in the search area (below the last detected instance). The program will look for the next instance below the current instance (whose quality is higher), which may cause the instances of poor quality located above the instance with higher quality not to be detected at all.
Note.It recommended that you specify a Nearest relation for a subelement in the group, defining its position relative to the to edge of the page. Otherwise, the program will select the next instance of the group by applying the best quality criterion to all the instances in the search area (below the last detected instance). The program will look for the next instance below the current instance (whose quality is higher), which may cause the instances of poor quality located above the instance with higher quality not to be detected at all.
See also:
Creating, copying, and deleting elements
12.04.2024 18:16:02