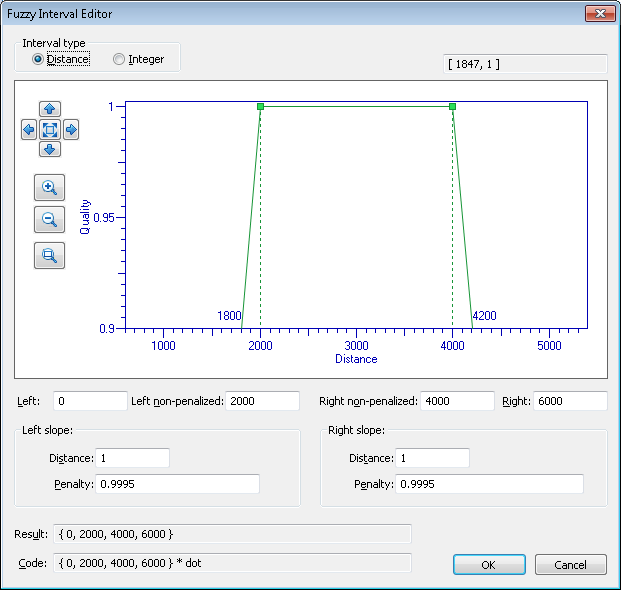
Fuzzy interval visual editor
ABBYY FlexiLayout Studio offers a visual editor to make specifying fuzzy intervals easier. You can open the fuzzy interval editor from the Properties dialog box of a Character String element (Character String tab,  button) or from the main menu by selecting Tools → Fuzzy Interval Editor….
button) or from the main menu by selecting Tools → Fuzzy Interval Editor….
Show Fuzzy Interval Editor dialog box
This dialog box displays a graph representation of the fuzzy interval. The vertical axis measures the quality of the hypothesis and the horizontal axis measures the linear dimensions or the number of characters. Coordinates of the intersection of the fuzzy interval borders with the horizontal axis are also displayed on the graph.
The "Zoom in" and "Zoom out" buttons change the horizontal and vertical scales synchronously. You can also zoom a selected image area using the Zoom selected area button. The 


 buttons allow you to move the area in the corresponding direction. To fit the interval, click
buttons allow you to move the area in the corresponding direction. To fit the interval, click  .
.
The fields below the graph contain the numerical values of the interval. You can specify the interval either by editing the graph with your mouse or by entering the desired numerical values in the corresponding fields.
The visual fuzzy interval editor operates in two modes:
- Fuzzy intervals for units of measurement, which may be fractional. In this case, select Distance under Interval type.
 Note.
Note. - Fuzzy intervals for positive integers, such as string length in characters. In this case, select Integer under Interval type.
 Note.If you open the fuzzy interval editor from the Properties dialog box of a Character String element, one of the two modes is automatically selected depending on the field from which you called the editor.
Note.If you open the fuzzy interval editor from the Properties dialog box of a Character String element, one of the two modes is automatically selected depending on the field from which you called the editor.
Editing the graph
You can change the interval by moving the green markers to the right or to the left with your mouse. You can also change the angle of the slopes. Certain restrictions apply: you cannot move the left marker to the right of the right marker, etc. The corresponding numerical values will be displayed in the fields below the graph.
Changing the numerical values directly
The Left, Left non-penalized, Right, and Right non-penalized fields correspond to the representation of the fuzzy interval in the program. Left and Right are the extreme points, Left non-penalized and Right non-penalized are the non-penalized points. The Left slope and Right slope groups set the slope of the sides of the graph, which represent the penalty coefficient for deviating by a Distance from the non-penalized point. Changing a slope moves the corresponding extreme point without changing the non-penalized point. Changing an extreme and non-penalized point results in changes in the corresponding slope. When you edit fields, the depiction and the values of the dependent fields are changed accordingly.
Saving the results
If the fuzzy interval editor was called from the Properties dialog box of a Character String element, clicking OK will automatically insert the fuzzy interval into the corresponding field of the dialog box.
If the fuzzy interval editor was called from the Tools menu, you can copy the fuzzy interval from the Result field or from the Code field. The purpose of the Code field is to allow you to paste the code into the code on the Advanced tab, for example, when using a fuzzy interval as an argument of the FuzzyQuality function.
4/12/2024 6:16:02 PM