Choosing the optimal number of processes and CPU cores
There are two separate parameters in the properties of a Processing Station, the CPU cores and the number of processes:
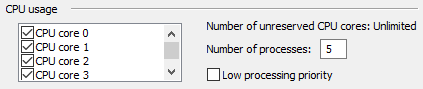
The CPU core 0, 1, etc. are the CPU cores that are available to the given Processing Station. Each CPU core is listed separately and can be either enabled or disabled by selecting or clearing the respective check box.
- If you need to reserve one or two CPU cores on the given Processing Station for tasks other than OCR, clear the check boxes next to the respective CPU cores in the Properties dialog box.
- If the Server Manager and the Processing Station are installed on one and the same computer, consider restricting the number of CPU cores available to the Processing Station.
- If the Server Manager controls a large number of remote Processing Stations, we do not recommend installing a Processing Station on the computer hosting the Server Manager.
The number of processes is the number of OCR and document conversion processes simultaneously executed on the given Processing Station. The processes are completely independent from one another—when a process completes OCR on one file, it sends the result to the Server Manager and immediately picks up another file from the queue, while the other processes are busy recognizing their own files.
By default, the number of processes on each Processing Station is set to n+1, where n is the number of CPU cores on the station. This is the recommended setting for A4 pages that contain mostly printed text.
FineReader Server supports hyper-threading, but virtual cores will not be displayed in the Processing Station settings. For Processing Stations powered by HT CPUs, set the number of processes to 2n+1, where n is the number of processor cores on the Processing Station.
You may want to change the default setting in the following cases:
- If you need to process a large number of very small files and a lot if time is spent sending files back and forth between the Server Manager and a Processing Station. The CPUs on the Processing Station will be idle while waiting for files to arrive, so it would be a good idea to increase the number of processes to have the workload more evenly distributed among the CPUs.
- Processing very large files may require a lot of RAM. If you see jobs terminating with a "Not enough memory" error message, try reducing the number of processes on the corresponding Processing Station. Fewer processes means fewer files processed simultaneously and smaller demands on RAM.
3/26/2024 1:49:49 PM